In the ever-evolving world of technology, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are reshaping how we interact with digital content. These immersive technologies are not just for gaming anymore; they’re revolutionizing industries from education to healthcare, offering experiences that were once the stuff of science fiction. As AR and VR continue to advance, the applications become increasingly innovative, transforming everyday tasks and entertainment.
Developers are now creating AR and VR apps that allow users to visualize furniture in their homes before purchasing, learn new skills through interactive tutorials, and even explore distant planets. These applications are making waves by enhancing user engagement and providing unique ways to interact with the world. As more people adopt these technologies, the potential for AR and VR apps expands, promising a future where digital and physical realities merge seamlessly.
Ar Vr Apps
 Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) apps have roots tracing back several decades, with early conceptualizations and experimental applications appearing in the 1960s and 1970s. These technologies began primarily with scientific and military uses, gradually transitioning into the mainstream as hardware became more accessible. In the early 1990s, AR was used to enhance visual experiences by overlaying digital images and data onto the real world. By the late 2000s, VR had garnered attention for its immersive environments, which were then primarily leveraged in gaming and simulations.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) apps have roots tracing back several decades, with early conceptualizations and experimental applications appearing in the 1960s and 1970s. These technologies began primarily with scientific and military uses, gradually transitioning into the mainstream as hardware became more accessible. In the early 1990s, AR was used to enhance visual experiences by overlaying digital images and data onto the real world. By the late 2000s, VR had garnered attention for its immersive environments, which were then primarily leveraged in gaming and simulations.
Recent Advancements in AR and VR
In the past few years, AR and VR technologies have undergone significant developments, accelerating their adoption across various sectors. Today’s AR apps leverage sophisticated AI to improve image recognition, depth perception, and real-time information overlay, making them more intuitive and interactive. Meanwhile, VR apps have seen improvements in display technology, motion tracking, and user interface design, enhancing the immersive experience with higher resolutions and more responsive controls. These advancements contribute to more robust applications in fields like education, where students explore complex subjects through interactive simulations, or in healthcare, where surgeons perform procedures with precision using real-time 3D models.
Applications of AR and VR in Various Industries
Education and Training
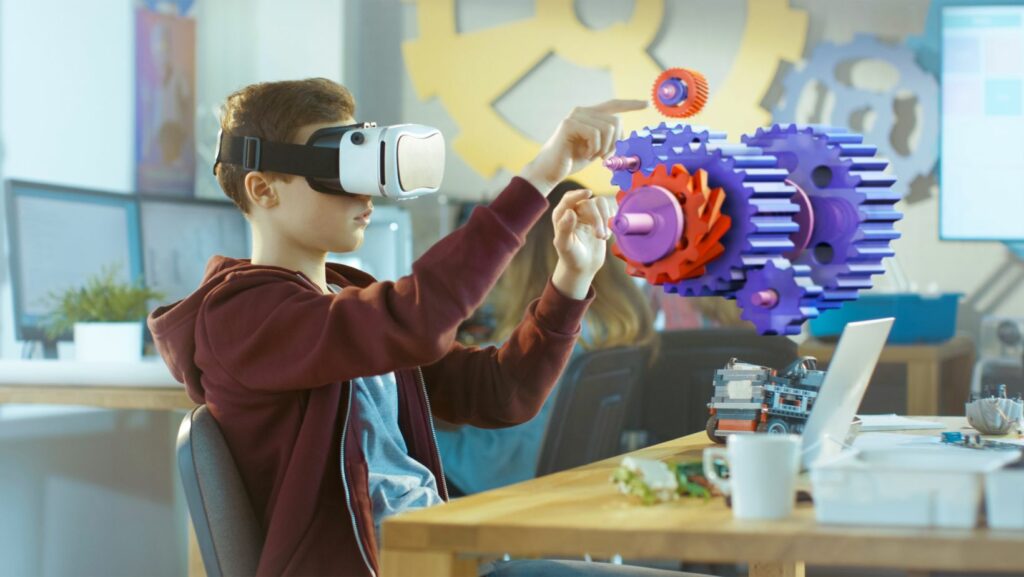
 AR and VR technologies revolutionize traditional learning and training methods. AR apps bring interactive elements to educational content, making complex subjects like biology or astronomy more accessible by overlaying digital information onto real-world objects. For instance, students can explore the human anatomy in 3D without the need for physical models. Similarly, VR creates immersive learning environments that simulate real-life scenarios for skills training. Pilots use VR for flight simulations, providing them with hands-on experience without the risks associated with actual flying.
AR and VR technologies revolutionize traditional learning and training methods. AR apps bring interactive elements to educational content, making complex subjects like biology or astronomy more accessible by overlaying digital information onto real-world objects. For instance, students can explore the human anatomy in 3D without the need for physical models. Similarly, VR creates immersive learning environments that simulate real-life scenarios for skills training. Pilots use VR for flight simulations, providing them with hands-on experience without the risks associated with actual flying.
Retail and Marketing
In the retail sector, AR and VR apps transform shopping experiences and marketing strategies. AR allows customers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase. For example, furniture retailers offer AR apps that enable shoppers to see how a sofa would look in their living room. VR takes customer engagement further by placing them inside virtual stores, where they can browse and interact with products as if they were physically present, enhancing customer satisfaction and boosting sales.These applications are making waves by enhancing user engagement and providing unique ways to interact with the world. As more people adopt these technologies, the potential for AR and VR apps expands, promising a future where digital and physical realities merge seamlessly.
Healthcare and Therapy
 The healthcare industry benefits significantly from AR and VR applications, improving both patient care and medical training. AR helps surgeons perform precise surgeries by projecting vital data directly onto their field of view during procedures. This reduces the need for invasive methods and increases the accuracy of operations. VR assists in therapy by providing controlled environments for patients undergoing physical rehabilitation, allowing them to practice motions in a safe, repeatable space. It also supports mental health treatments by exposing patients to virtual situations that help them cope with conditions like PTSD or anxiety.
The healthcare industry benefits significantly from AR and VR applications, improving both patient care and medical training. AR helps surgeons perform precise surgeries by projecting vital data directly onto their field of view during procedures. This reduces the need for invasive methods and increases the accuracy of operations. VR assists in therapy by providing controlled environments for patients undergoing physical rehabilitation, allowing them to practice motions in a safe, repeatable space. It also supports mental health treatments by exposing patients to virtual situations that help them cope with conditions like PTSD or anxiety.
Overall, AR and VR technologies are pivotal across various industries, dramatically enhancing how professionals work, how consumers shop, and how patients receive care, echoing the integration trends seen in the education and healthcare sectors as highlighted earlier in the article.